Lightning Arrester
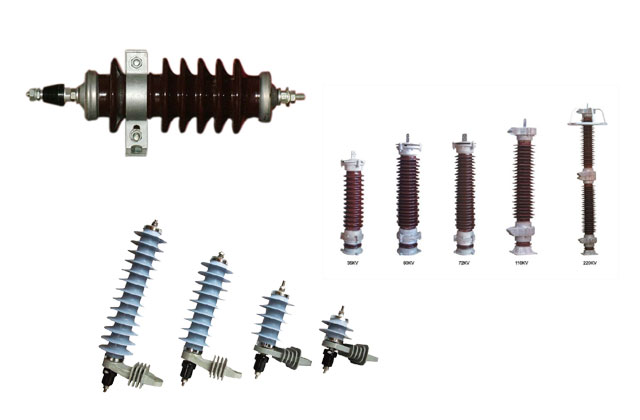
Manufacturer, Exporters, Dealers, and Suppliers of Lightning Arrester in ahmedabad, gujarat, india
Features
- Function : It diverts the surge voltage to the ground and protects the electrical insulation and conductors from damage.
- Construction : Consists of non-linear resistors (often zinc oxide, ZnO) housed in a weather-resistant enclosure (porcelain or polymer).
- Operating Principle : Under normal voltage, it offers high resistance. When a high surge voltage occurs, its resistance drops drastically, allowing the surge current to pass safely to the ground.
Types of Lightning Arresters
- Station Type Arrester – For substations and major installations.
- Intermediate Type Arrester – For medium-voltage lines.
- Distribution Type Arrester – Used on distribution transformers and lines (11kV/22kV/33kV).
- Expulsion Type Arrester – Older design, less common now.
- Metal-Oxide Gapless Arrester (MOG) – Modern, highly reliable type without spark gaps.
Advantages
- Prevents equipment damage due to voltage surges.
- Enhances system reliability and safety.
- Requires minimal maintenance, especially gapless types.
Applications
- Power transformers
- Switchgear
- Overhead transmission lines
- Distribution panels and substations
Best Quality Lightning Arrester Suppliers In Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India.
Lightning Arrester is a protective device used in electrical power systems to safeguard equipment from high-voltage transients caused by lightning strikes or switching surges. It is installed at strategic locations such as transformer terminals, transmission line ends, and substations.
lightning arrester is an essential component in the realm of electrical safety, specifically engineered to shield electrical systems from the potentially catastrophic effects of lightning strikes. When lightning occurs, it generates an immense surge of electrical energy that can wreak havoc on unprotected systems, leading to equipment failure, data loss, and even fire hazards. The primary function of a lightning arrester is to provide a low-resistance pathway for this electrical discharge, effectively diverting the surge away from sensitive equipment and directing it safely into the ground. This diversion not only protects the integrity of the electrical system but also ensures the continued operation of critical infrastructure, which is particularly vital in sectors such as telecommunications, power generation, and data centers.
To maximize the effectiveness of lightning arresters, proper installation and regular maintenance are paramount. The installation process must adhere to established guidelines and standards to ensure that the arrester is positioned correctly and connected to a reliable grounding system. This involves selecting the appropriate type of arrester based on the specific requirements of the electrical system and the geographical location, as areas with frequent thunderstorms may necessitate more robust protection. Furthermore, routine inspections and maintenance are crucial to identify any wear and tear or potential failures in the system. This proactive approach not only extends the lifespan of the lightning arrester but also enhances the overall safety and reliability of the electrical installations.
In addition to protecting equipment, lightning arresters play a significant role in safeguarding human life. By mitigating the risks associated with lightning strikes, these devices contribute to a safer environment for workers and the general public. In industries where electrical systems are integral to operations, such as manufacturing and healthcare, the presence of a well-maintained lightning protection system can prevent costly downtime and ensure that essential services remain uninterrupted during adverse weather conditions. As climate change continues to influence weather patterns, leading to more frequent and severe storms, the importance of lightning arresters in protecting both infrastructure and human safety cannot be overstated. Investing in these protective devices is not merely a precaution; it is a critical strategy for resilience in an increasingly unpredictable world.


